Magento Vs Drupal Vs WordPress: Choosing the Right CMS for Your Website
Choosing the right Content Management System (CMS) for your website can be a challenging decision, especially when considering popular options like Magento, Drupal, and WordPress. Each platform offers unique features, functionalities, and adaptabilities that cater to different types of websites and business needs.
In this blog, we delve into a comprehensive comparison of “Magento Vs Drupal Vs WordPress,” exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and best use-cases. Whether you’re building an e-commerce site, a content-heavy platform, or a versatile business website, this guide will provide valuable insights to help you make an informed decision configured to your specific requirements.
Understanding CMS: The Foundation of Modern Website Management
In the digital age, a Content Management System (CMS) is essential, serving as the foundation for creating, managing, and optimizing digital content. Essentially, a CMS offers a user-friendly platform that enables individuals of all skill levels to easily contribute and oversee content.
This system streamlines the process of web development by offering a centralized interface where content can be created, edited, and published. It eliminates the need for complex coding, making website maintenance more accessible to a broader range of users.
Technically, CMS platforms are diverse, ranging from simple website builders to sophisticated systems that can manage large-scale enterprise content. They are built on a database that stores content, metadata, and other information which is then displayed through a set of templates. This separation of content from design allows for dynamic content management and presentation.
Advanced CMSs also provide tools for SEO, analytics, and customization, enabling businesses to alter their digital presence to specific audience needs and market trends. These systems can support various plugins and integrations, allowing for extended functionality and scalability to meet evolving business requirements.
Why CMS is Important:
- Scalability: A good CMS can handle increasing amounts of traffic and content without performance degradation.
- Security: It offers strong security features to protect against cyber threats.
- Compatibility: Ensures compatibility with various plugins and third-party applications, enhancing functionality.
- Data Management: Efficient handling and storage of large volumes of data.
- API Support: Provides API integrations for extending functionality and connecting with external systems.
- Customization: Allows technical customization to meet specific business requirements.
- Performance Optimization: Optimizes website loading times and overall performance.
An Introduction to WordPress: Exploring its Features and Capabilities
WordPress is a widely acclaimed Content Management System (CMS) known for its versatility and ease of use. Originally a blogging platform, WordPress has evolved into a comprehensive tool for creating a wide range of websites, from simple blogs to complex e-commerce sites.
Its user-friendly interface, combined with a vast library of themes and plugins, makes it a popular choice for both beginners and seasoned web developers. The platform is not only highly customizable but also SEO-friendly, enhancing its appeal to businesses seeking to improve their online presence.
WordPress’s open-source nature encourages a vibrant community contribution, continually adding to its functionality and versatility.
Exploring the Distinctive Features of WordPress
- Gutenberg Editor: A block-based editor that revolutionizes content layout and design, making complex layouts easy to manage.
- Custom Post Types and Taxonomies: Allows for the creation of different content types beyond just posts and pages, customized to specific needs.
- Multisite Functionality: Enables running multiple sites from a single WordPress installation, a powerful tool for businesses and networks.
- REST API: Facilitates integration with other systems and applications, allowing WordPress to serve as a backend for mobile apps and other web services.
- Diverse Themes and Plugins: Provides a vast array of customizable themes and plugins for enhanced website functionality.
- E-Commerce Flexibility: Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses with sturdy e-commerce solutions.
- MySQL Compatibility: Efficiently works with the MySQL database system.
Exploring the Technical Challenges of WordPress
- Resource-Heavy Plugins: Some plugins are poorly coded, leading to resource-intensive operations that slow down the website.
- Security Patching: Frequent need for security updates due to its popularity makes it a prime target for exploits if not regularly maintained.
- Database Overhead: Over time, WordPress databases can become bloated, affecting website performance and loading times.
- SEO Optimization Dependency: Optimal search engine ranking often requires additional plugins and continuous SEO strategy adjustments.
- Compatibility Issues: With each update, there’s a risk of theme and plugin incompatibilities, potentially breaking site functionality.
- Limited Advanced Customizations: For complex, highly-customized websites, WordPress might require extensive coding, surpassing the basic PHP and HTML/CSS knowledge.
Exploring Magento: A Deep Dive into the Advanced E-commerce Platform
Magento’s technical prowess extends to its Durable back-end operations, which support intricate analytics and reporting features. It allows for detailed tracking of customer behavior and sales trends, crucial for data-driven decision-making.
Magento’s API framework facilitates seamless integration with a variety of third-party services and systems, including payment gateways, shipping services, and CRM tools. Its emphasis on responsive design ensures that e-commerce sites are mobile-friendly, a critical factor in today’s digital Domain.
Additionally, Magento’s multi-website and multi-store functionality enable businesses to manage multiple e-commerce sites from a single admin interface, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency.
Key Benefits of Implementing Magento
- Modular Architecture: Magento’s open-source framework allows for extensive technical customization and scalability.
- Advanced Database Management: Efficiently handles complex and large product catalogs, supporting sophisticated data operations.
- API Integration: Powerful API support enables seamless connection with a wide array of external systems and applications.
- Performance Tools: Includes advanced caching mechanisms and database optimization features for high-performance websites.
- SEO Optimization: Designed with SEO best practices, enhancing search engine visibility.
- Multi-Store Functionality: Capable of managing multiple e-commerce stores from a single backend interface, streamlining operations.
Challenges and Setbacks of Implementing Magento
- High Resource Requirements: Magento’s advanced functionality demands significant server resources, which can lead to higher hosting costs.
- Complex Architecture: Its complex architecture makes customization and troubleshooting more challenging, requiring specialized technical knowledge.
- Performance Optimization Needs: Without proper technical optimization, Magento can suffer from slow load times, impacting user experience.
- Frequent and Complex Updates: Regular updates are crucial for security and functionality but can be technically challenging to implement.
- Developer Dependency: Customizing and maintaining Magento often requires reliance on skilled developers.
- Limited Hosting Options: Due to its resource intensity, Magento may not perform optimally on standard hosting services, necessitating specialized Magento hosting solutions.
Understanding Drupal: A Comprehensive Guide to the Powerful CMS
Drupal is an open-source content management system (CMS) notable for its robustness and flexibility, especially suited for complex, content-rich websites and web applications. Technically, Drupal excels with its modular structure, allowing for extensive customization through a variety of modules and themes.
It’s known for strong security features, making it a preferred choice for government and enterprise-level websites. Additionally, Drupal supports multilingual capabilities natively, making it ideal for international sites. Its scalability makes it capable of handling high traffic loads, and the system is designed to be extensible, accommodating a broad range of integration options.
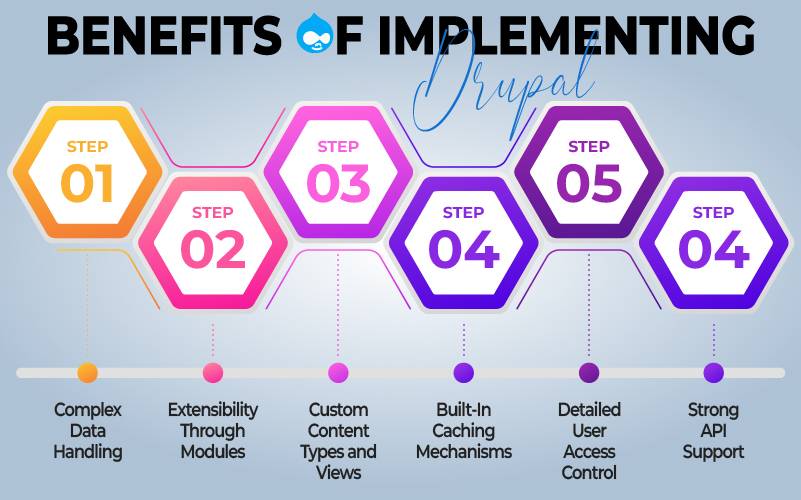
Benefits of Implementing Drupal
- Complex Data Handling: Drupal excels in managing complex data structures and relationships, ideal for data-intensive sites.
- Extensibility through Modules: Offers a wide range of modules that extend its core functionalities for various specialized needs.
- Custom Content Types and Views: Allows for the creation of unique content types and highly customizable views without extensive coding.
- Built-In Caching Mechanisms: Advanced caching for improved performance and load times.
- Strong API Support: Powerful API capabilities facilitate seamless third-party integrations and headless CMS architectures.
- Detailed User Access Control: Provides granular user permission settings, crucial for websites needing intricate access control systems.
Exploring the Limitation of Drupal for Website Development
- Complexity: Drupal’s advanced capabilities come with a steep learning curve, particularly for those without technical expertise.
- Resource Intensive: Requires more resources for optimal performance, potentially leading to higher hosting costs.
- Less Intuitive User Interface: The administrative interface can be less user-friendly compared to other CMS platforms.
- Development Time: Customizing Drupal often demands more time and developer resources.
- Community Size: While strong, its community is smaller compared to other major platforms like WordPress, which can affect the availability of resources and support.
- Update Management: Keeping Drupal updated can be challenging, requiring attention to maintain site security and functionality.
Evaluating E-commerce and CMS Platforms: Magento VS Drupal VS WordPress
Ease of Use
When considering the ease of use in website development platforms, WordPress, Drupal, and Magento each cater to different user needs. WordPress stands out for its exceptional user-friendliness, making it ideal for beginners or those seeking a hassle-free website creation experience.
Drupal, while Vigorous in features, is more complex and better suited for those with technical expertise, particularly for intricate, content-heavy sites. Magento, focusing on e-commerce, offers powerful tools but requires a deeper understanding of online retail systems, thus presenting a steeper learning curve than WordPress. These platforms exemplify the balance between functionality and user accessibility in the realm of website management.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Ease of installation | User-friendly with one-click installs from many web hosts. | More complex, suited for users with technical knowledge. | Relatively complex, often requiring technical skills for installation. |
| User interface | Intuitive, featuring a visual editor and drag-and-drop functionality. | More technical, offering extensive control for experienced users. | Complex, designed for users with e-commerce and technical expertise. |
| Customizability | Highly customizable with themes and plugins; no coding needed. | Highly customizable with modules; requires technical knowledge. | Extremely customizable, especially for e-commerce, but requires technical expertise. |
| Content creation | Straightforward content management with a visual editor. | More technical, ideal for complex content structures. | Focused on e-commerce content, requires understanding of e-commerce principles. |
| Community support | Large, supportive community with extensive resources and tutorials. | Strong community with a focus on technical and developer support. | Reliable community, particularly strong in e-commerce solutions. |
Customization
The customization capabilities of a content management system are pivotal for websites to specific needs. WordPress, Drupal, and Magento stand out in this arena, each offering distinct customization features.
WordPress is celebrated for its simplicity and a wide array of themes and plugins, making it ideal for beginners and general-purpose websites. Drupal offers advanced technical customization suited for complex, data-driven sites. Magento, with its focus on e-commerce, provides specialized customization options for online retail. Let’s delve into how each platform fares in various customization parameters.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Themes and templates | Wide range of both free and premium themes. | Numerous themes with a focus on data-driven websites. | E-commerce focused themes, both free and premium. |
| Plugins and extensions | Extensive plugins for various functionalities. | Modules for various functionalities, with a focus on data management. | Extensions focused on e-commerce functionalities. |
| Code customization | Code customization possible for advanced users. | Highly customizable at the code level for developers. | Advanced customization capabilities, particularly for e-commerce. |
| User roles and permissions | Customizable roles and permissions. | Advanced user role and permission customization. | Comprehensive role and permission customization, made for e-commerce. |
Security
In the realm of website security, WordPress, Drupal, and Magento each offer unique strengths. WordPress, popular for its user-friendliness, counters its vulnerability as a common attack target with frequent updates and a vast array of security plugins.
Drupal is renowned for its enterprise-level security, making it ideal for sites requiring stringent data protection. Magento, modified for e-commerce, focuses heavily on secure transactions, essential for online retail platforms. Thus, each system caters to varying security needs, from general website protection to advanced data security.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Security updates | Regular updates for security. | Frequent, thorough security updates. | Regular updates, with a focus on e-commerce security. |
| Third-party plugins and extensions | Large selection, varying in quality. | Quality modules with a focus on security. | E-commerce focused extensions with an emphasis on secure transactions. |
Support
In terms of support, WordPress VS Drupal VS Magento each provide Powerful resources to assist their users. WordPress boasts a vast, active community, offering extensive support through forums, guides, and tutorials, ideal for users at all levels.
Drupal’s support network is particularly strong among developers and technical users, with comprehensive documentation and a dedicated online community for complex issue resolution.
Magento, catering to the e-commerce sector, provides specialized support, including detailed documentation and a community focused on retail-specific solutions. Each platform ensures users have access to the necessary resources, whether for simple blog setups or complex e-commerce sites.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Official documentation | Comprehensive and user-friendly documentation. | In-depth documentation, technical in nature. | Extensive documentation with a focus on e-commerce. |
| Community support | Large, helpful community across many forums. | Technical and developer-focused community support. | Strong support community, especially in e-commerce aspects. |
| Paid support | Available through third-party services. | Available through various service providers. | Professional support available, often e-commerce focused. |
Cost
In terms of cost, WordPress VS Drupal VS Magento present different financial considerations. WordPress offers a cost-effective solution with free core software and a wide range of themes and plugins, though premium options can increase costs.
Drupal, while free to use, may incur higher costs for advanced customization and technical expertise. Magento, made for e-commerce, offers a free version but can become costly with premium features and specialized hosting requirements, particularly for its enterprise edition.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Software cost | Free, open-source software. | Free, open-source software. | Free Community version; Enterprise version is paid. |
| Hosting cost | Varies based on hosting provider. | Depends on hosting choice; can be higher for high-performance sites. | Often higher due to resource-intensive nature. |
| Themes and plugins cost | Both free and paid options are available. | Both free and paid modules are available. | Both free and paid extensions, with some premium e-commerce options. |
Popularity
Regarding popularity, WordPress leads as the most widely used CMS, favored for its user-friendliness and versatility, making it a top choice for a diverse range of websites. Drupal, while less popular than WordPress, is highly regarded in professional and technical circles for its robustness and scalability, especially for complex sites.
Magento, though it has a narrower focus on e-commerce, enjoys significant popularity in the online retail space due to its specialized features. Each platform has carved out its niche, with WordPress dominating general web development, Drupal excelling in complex web projects, and Magento being a go-to for e-commerce ventures.
| Parameter | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Market share | Highly popular for a wide range of websites. | Popular, especially for complex, data-driven websites. | Highly popular in the e-commerce sector. |
| User community | Largest user community, very active. | Smaller than WordPress, but very dedicated. | Focused on e-commerce, with a strong business community. |
| Third-party resources | Extensive resources for various needs. | Strong resources, especially for developers. | Numerous e-commerce specific resources and integrations. |
Functionalities
In terms of functionalities, WordPress, Drupal, and Magento each excel in different areas. WordPress is known for its simplicity and a wide array of user-friendly features, making it ideal for content-oriented websites and blogs.
Drupal offers more complex functionalities, including advanced user permissions and custom content types, suited for data-intensive and complex websites. Magento, specifically designed for e-commerce, provides strong functionalities like inventory management, advanced payment gateways, and customer segmentation, catering to the comprehensive needs of online stores.
| Functionality | WordPress | Drupal | Magento |
| Core Purpose | Content Management System (CMS) focused on ease of use and simplicity. | CMS is known for its flexibility and scalability, catering to complex content management needs. | E-commerce platform designed for managing and scaling online stores. |
| Custom Content Types | Basic custom content types with plugins. | Advanced custom content types natively supported. | E-commerce oriented content types, like products and categories. |
| User Access Control | Basic access control with plugins for advanced needs. | Granular access control with sophisticated user permission management. | Advanced user roles and permissions, adapted for e-commerce. |
| Multilingual Support | Basic through plugins. | Advanced multilingual features built-in. | Multilingual support geared towards global e-commerce. |
| Performance and Scalability | Good for small to medium-sized websites. | Excellent for large and complex websites requiring scalability. | High performance and scalability, especially for large e-commerce sites. |
| SEO Capabilities | Good with SEO plugins. | Advanced SEO capabilities with modules. | Strong SEO features, particularly for e-commerce. |
| Caching and Optimization | Basic caching with plugins for enhancement. | Advanced caching mechanisms for performance optimization. | Sophisticated caching and performance optimization, crucial for e-commerce. |
| Security | Good, with plugins for enhanced security. | Very strong, with an emphasis on enterprise-level security. | Strong, with a focus on secure e-commerce transactions. |
| Theme System | Wide range of themes, easy to customize. | Theming system that allows for well-built customization. | Theme structure focused on e-commerce, customizable for branding. |
| Plugin/Module/Extension Ecosystem | Extensive range of plugins for various features. | Wide range of modules for extending functionality. | E-commerce focused extensions for additional features. |
| API Support | REST API for integration and application development. | Strong API support for integration and headless CMS capabilities. | Strong API capabilities for integrating various e-commerce systems and apps. |
| Content Workflow | Basic workflow, enhanced with plugins. | Advanced workflow capabilities for content publishing. | Workflow altered for e-commerce operations. |
| E-commerce Capabilities | Basic with e-commerce plugins (like WooCommerce). | Possible with e-commerce modules, but not a core focus. | Core functionality, optimized for all aspects of e-commerce. |
Conclusion:
In summary, when comparing Magento, Drupal, and WordPress, each platform has its own strengths suited for different web projects. WordPress is known for its ease of use and versatility, making it great for various websites, especially those needing lots of plugins.
Drupal is preferred for its advanced customization and handling complex data, making it a top choice for developers working on large, content-rich sites. Meanwhile, Magento is designed for businesses aiming to create robust online stores with powerful e-commerce features.
Ultimately, the decision between WordPress, Drupal, and Magento depends on the project’s specific requirements, whether it’s a simple blog, a data-heavy site, or a comprehensive e-commerce platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can I switch my website from one of these platforms to another easily?
Switching between these platforms can be challenging and depends on the complexity of your website. It often requires technical expertise, especially when moving to or from Drupal or Magento.
-
Which platform is the best for SEO?
WordPress is often praised for its SEO-friendly plugins, but Drupal and Magento also offer Durable SEO tools. The best platform for SEO depends on how well you utilize each platform’s capabilities.
-
Is Magento only suitable for e-commerce websites?
Magento is primarily designed for e-commerce, offering specialized tools for online stores. While it can be used for other types of sites, its features are overkill for non-e-commerce purposes.
-
Can I use Drupal or Magento without coding knowledge?
While basic site management is possible, fully leveraging Drupal and Magento’s advanced features typically requires some coding knowledge. In contrast, WordPress is more accessible for users without coding skills.
-
How do the security features of these platforms compare?
Drupal is known for its strong security features, making it a favorite for enterprise-level sites. WordPress, while secure, requires careful management of plugins for optimal security. Magento offers specialized security features for e-commerce.
-
Which platform is best for a large website with heavy traffic?
Drupal is well-suited for handling large, complex sites with heavy traffic, due to its robust performance and scalability. Magento also performs well under heavy traffic, particularly for e-commerce sites.
-
Is community support available for all three platforms?
Yes, WordPress, Drupal, and Magento all have active communities. WordPress has the largest community, while Drupal and Magento have more specialized communities.
-
How often do these platforms receive updates?
All three platforms are regularly updated. WordPress updates are more frequent, while Drupal and Magento updates are typically more substantial.
-
Can I run an online store on WordPress or Drupal?
Yes, with plugins like WooCommerce for WordPress and e-commerce modules for Drupal, you can run online stores, though Magento is specifically built for e-commerce.
-
Are there any cost advantages to using one platform over the others?
WordPress generally has lower initial costs due to its user-friendly nature and free plugins. Drupal and Magento can be more costly due to development and maintenance expenses, especially for Magento’s enterprise features.